Computing Feasible RIS Positions
This tutorial explains how to determine the feasible RIS positions based on the location of the transmitter and the RIS target point(s).
Note
Before executing this step, you must first compute and visualize the transmitter-only coverage map. Please follow the Computing Transmitter-Only Coverage Map tutorial beforehand.
There are two ways to define the RIS target points:
Using the Target Points from Clustering:
Note
To use this option, you must first run the clustering algorithm to compute target points. Refer to the Finding RIS Target Points via K-means Clustering tutorial before proceeding.
In the GUI, select the radio button “Use the target point(s) found via clustering algorithm”. This will use the previously computed RIS target points to determine feasible RIS positions.
Manually Entering Target Point Coordinates:
Go to the labelframe “Manual trials” on the left side of the GUI.
Enter the number of RIS target points in the field “Number of target points”
Select the checkbox “Enter the target point(s) manually”.
A new input area will appear between the labelframe “Manual trials” and the labelframe “Optimization algorithm”.
Enter the x, y, z coordinates for each target point manually.
Final Step: Compute Feasible RIS Positions
After selecting or entering the target points, press the button “Compute feasible RIS positions”.
This will compute all feasible RIS positions that have line-of-sight (LoS) to both the transmitter and all RIS target points.
After execution:
A binary poor coverage map is displayed.
Target points are shown as green ‘X’ symbols.
Feasible RIS positions are marked with green star symbols.
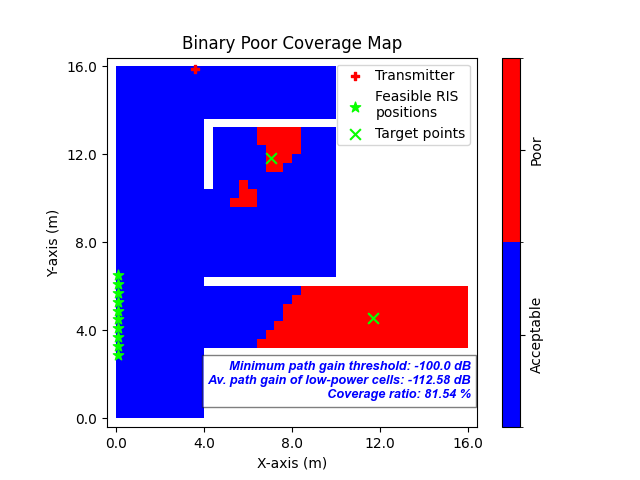
Fig. 1: Binary poor coverage map showing RIS target points (green ‘X’) and feasible RIS positions (green stars)